Embedded Finance: Everything You Need to Know
Embedded finance directly integrates financial services like payments, lending, insurance, or investments into non-financial platforms or applications. This allows businesses outside traditional financial institutions to offer these services within their existing products, creating a seamless user experience. For example, a retail app might offer financing options at checkout without requiring customers to go through a separate bank or lender. Embedded finance aims to make financial services more accessible, convenient, and tailored to specific user needs, often enhancing customer engagement and generating additional revenue streams for the businesses involved.
The growing trend of embedded finance is transforming how financial services are delivered. It allows businesses in various industries to offer banking-like services without needing to become full-fledged banks. This approach benefits consumers by providing a more integrated and user-friendly experience and helps companies increase customer engagement and create new revenue streams.
What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance is the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial platforms and apps. Rather than visiting a bank's website or opening a separate app, users can access financial services directly within the context of another service they are already using. This could involve making payments, securing loans, or managing investments within a retailer's app or through a ride-hailing service. Embedded finance is becoming a crucial element in the digital economy, offering enhanced convenience and a more streamlined user experience.
Examples of Embedded Finance
Embedded finance is becoming increasingly common across various sectors, from retail to technology. Here are some embedded banking examples across various industries:
- E-Commerce: Platforms like Amazon offer "Amazon Pay" and installment payment options directly at checkout, allowing customers to pay without leaving the site or using a traditional bank or credit card service.
- Ride-Hailing: Uber integrates payment processing directly into its app, allowing both customers and drivers to handle payments seamlessly without using a separate financial platform.
- Retail: Starbucks’ mobile app allows users to pay for their orders, reload their accounts, and even earn rewards, all embedded within the app.
- Gig Economy: Platforms like Swaplance provide freelancers with embedded payment solutions, enabling them to receive payments directly through the platform.
- Insurance: Car rental companies like Turo offer embedded insurance options directly within their platform, allowing users to purchase coverage as part of the rental process.
These examples illustrate how embedded finance is becoming integral to the customer experience in various sectors, making financial services more accessible and integrated into everyday activities.
Embedded Payments: Definition and Examples
Embedded payments refer to payment systems directly integrated into a service or platform, enabling users to complete transactions without switching to another payment service or application. For instance, online retailers often integrate payment processing directly into their checkout process, allowing customers to pay using stored payment methods without leaving the site. Embedded payments can also be seen in subscription services, where payments are processed automatically through the app. Examples of embedded payments include platforms like Shopify, where payment processing is seamlessly integrated into the e-commerce experience, or the "buy now, pay later" options embedded in various online shopping platforms, or Apple Pay, which allows users to make purchases within apps or on websites with a single touch, using the payment information already stored on their device.
Embedded Banking: Definition and Applications
Embedded banking refers to integrating banking services, such as account management, payments, lending, and other financial services, directly into non-banking platforms, apps, or digital experiences. Unlike traditional banking, where customers interact directly with a bank, embedded banking allows users to access these financial services in everyday activities, such as shopping online, using a rideshare app, or managing business operations through a software platform.
Applications of Embedded Banking
Along with E-Commerce Platforms like Amazon and Shopify or Gig Economy Platforms like Uber, which we mentioned above, the following applications can be cited as examples:
- Business Software: Platforms like QuickBooks and Xero integrate banking services directly into their accounting and business management software. Small businesses can manage their finances, make payments, and even apply for loans without switching between different systems.
- Retail Apps: Retailers like Walmart embed financial services such as credit, buy-now-pay-later options, and payment processing into their apps, providing customers with a seamless shopping and financial management experience.
- Fintech Apps: Fintech companies like Chime or Revolut offer embedded banking solutions that allow users to manage their money, make payments, and access financial products directly through their mobile apps.
These applications of embedded banking demonstrate how financial services are becoming more integrated into everyday experiences, making banking more accessible, convenient, and tailored to users' specific needs.
Embedded Lending and Financing
Embedded Lending is a financial service that integrates lending products directly into non-financial platforms, apps, or online experiences. It allows users to access credit without needing to engage with a traditional bank or lender directly. This concept allows businesses to offer loans, credit, or financing options seamlessly within their existing services, enhancing customer experience and streamlining the borrowing process.
An example of embedded lending in the e-commerce space is Klarna. It allows customers to split purchase payments into smaller installments directly at the point of sale.
Embedded Financing is a financial service that allows businesses to offer credit or financing options directly within their products, services, or platforms. This form of financing is seamlessly integrated into the customer experience, enabling consumers or businesses to access financing solutions such as loans, credit lines, or payment plans without leaving the platform they are currently using. Embedded financing is becoming increasingly popular across various industries as companies seek to provide their customers with more integrated, convenient financial solutions.
For instance, Affirm, as a BNPL service, partners with retailers and offers installment payments at checkout, or Stripe Capital provides financing options to businesses using Stripe's payment processing platform, allowing them to access funds directly related to their sales.
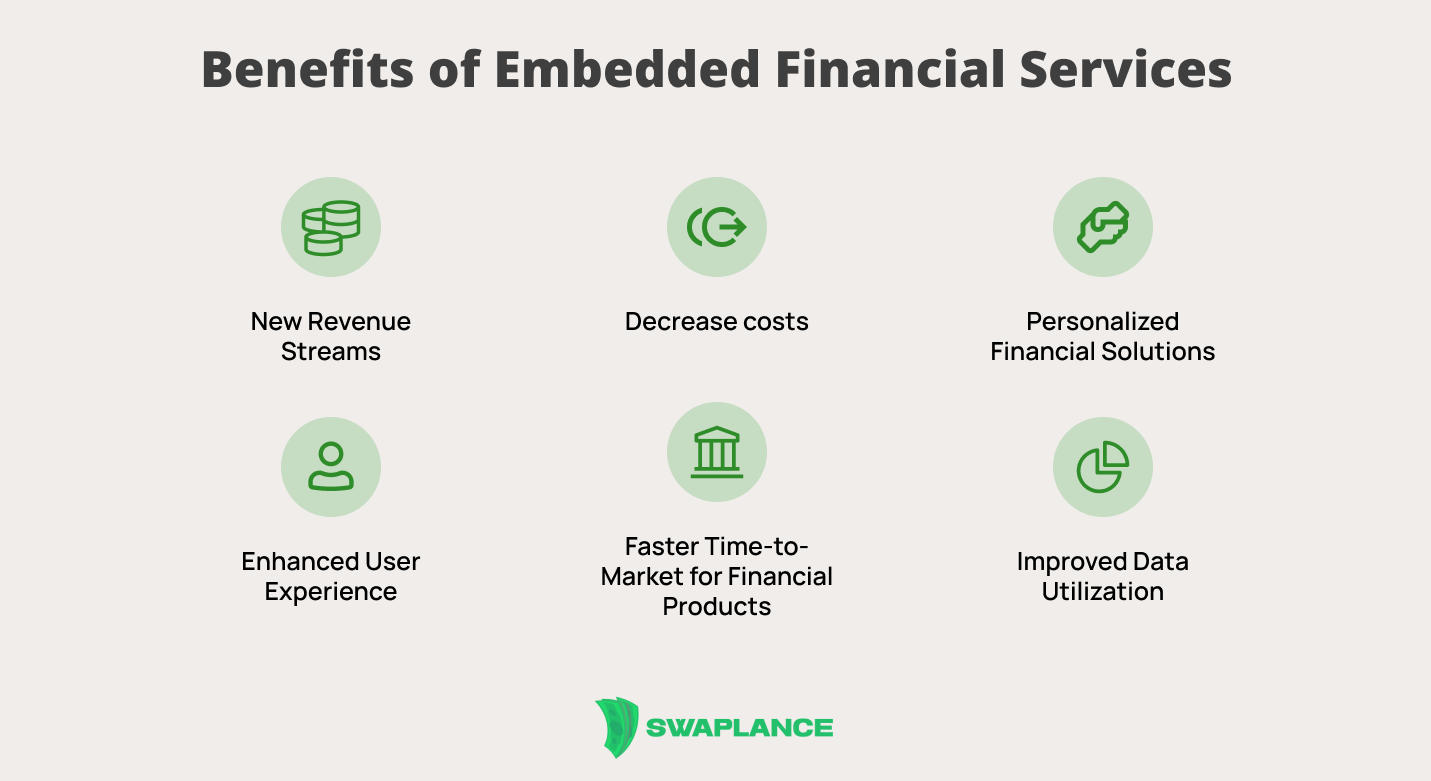
Benefits of Embedded Financial Services
Integrating financial services into existing platforms offers numerous benefits, including increased convenience, improved user experience, and greater accessibility to financial products. Businesses can enhance customer engagement by providing seamless payment, banking, or lending options without requiring users to leave their platforms. This convenience can lead to higher conversion rates and customer loyalty. Additionally, embedded financial services can open new revenue streams for companies, as they can offer financial products directly to their users. For example, embedded payments can reduce transaction friction, making it easier for customers to complete purchases.
Challenges and Risks in Embedded Finance
While offering many advantages, embedded finance also presents challenges and risks. One major challenge is the complexity of integrating financial services into non-financial platforms, which requires specialized knowledge and technology. There are also regulatory and compliance issues, as most regions heavily regulate financial services. Security is another significant concern, as integrating financial services into multiple platforms increases the risk of data breaches and fraud. Finally, there is the risk of dependency on third-party providers, which could lead to issues if those providers face difficulties.
Future Trends in Embedded Finance
The future of embedded finance is poised for significant growth, with more businesses across various sectors adopting these services to enhance their offerings. Key trends include the increasing adoption of embedded payments, the expansion of embedded banking services, and the rise of embedded insurance and investment products. Technological advances, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, are likely to drive the evolution of embedded finance further, making it even more integrated into everyday life. Swaplance, as a platform, is well-positioned to support businesses looking to stay ahead of these trends by connecting them with freelance experts who specialize in embedded finance integration.
Common questions
-
How do embedded payments improve the customer experience?Embedded payments improve the customer experience by offering a seamless and convenient way to make transactions directly within a platform or service. This eliminates the need for customers to be redirected to external payment gateways, streamlining the checkout process and reducing friction. Additionally, embedded payments often provide multiple payment options, such as buy-now-pay-later or instant financing, which enhances flexibility and satisfaction. The ease of use and speed associated with embedded payments can lead to higher conversion rates and a more positive overall customer experience.
-
What industries are adopting embedded finance solutions?Embedded finance solutions are being rapidly adopted across various industries, including fintech, e-commerce, gig economy, and retail. In fintech, companies are integrating financial services directly into their platforms, offering everything from payments to lending and insurance. E-commerce platforms are using embedded finance to offer seamless payment options, such as buy-now-pay-later, enhancing the customer experience. The gig economy leverages embedded financial tools to provide instant payments and financial services to workers. Retailers are also embedding finance solutions to offer loyalty programs, financing, and payment options directly within their shopping platforms.
-
What are the regulatory considerations for companies implementing embedded finance?Companies must navigate several regulatory considerations when implementing embedded finance to ensure compliance with financial laws and regulations. These include adhering to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, which mandate that companies verify the identity of their customers and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. Additionally, companies must consider data privacy laws, such as GDPR in Europe, which govern the collection and handling of customer data. Regulatory frameworks like the EU's Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) also play a role, as they dictate how financial data can be shared and accessed. Companies must work closely with legal and compliance teams to address these issues and ensure they meet all necessary regulatory standards when offering embedded financial services.
 Mark Petrenko
Mark Petrenko